Payment processing via Server-to-Server
If you wish to design your own forms for entering the payment data you can process your transactions in the background via a Server-to-Server connection. In this case your system saves payment details such as credit card numbers or bank account details and then creates a TLS socket-connection to the Server in order to process the payment. In this variant your system controls the communication with which involves more programming than with forms which automatically process the payments for you.
Process of a Server-to-Server payment
Notice: Please note that captures, credits and status inquiries are possible only via the Server-to-Server connection or via Batch.
Payment processing via Batch
Batch Manager lets you transmit payment transactions in the form of files. In this process you assemble transaction data such as the transaction ID, amount and currency in a batch file which you will later transmit to . then makes the payments and saves the transaction status in the batch file. After processing, the merchant can access the batch file with the details on the transaction status via download.
Security: Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
Where the credit card data is entered and stored is vital for the security of the credit card payments on the Internet. The card organisations have established a security program with the PCI security authorisation (Payment Card Industry) in order to guarantee the secure storage of credit card data. Please note that participation in PCI is compulsory and subject to a charge if you store credit card data. The key factor in this is the Merchant Interface variant:
1) HTML form
In this case the credit card data is only saved on the secure server. Optionally provides you with a pseudo card number (PKN), which can be used like a real credit card number.
2) Server-to-Server payment
Credit card data is saved on your systems. Therefore you are obliged under certain circumstances to undergo the MasterCard and VISA PCI Data Security program which is associated with annual authorisation costs and time. You can obtain further details from your credit card acquirer.
Notice: Please note that Visa and MasterCard have established strict security regulations for the protection of credit card data. Anyone who saves credit card numbers on their system or even only transmits such data must undergo –at their own expense - regular security authorisation. You should therefore use the forms. If you require credit card numbers for recurrent subscription payments, lets you use a pseudo card number which you can substitute for the real credit card number for authorisations, captures and credits.
3) Batch
Payment data can be submitted as Batch file to . In this case there are the two variants via the SFTP protocol and per HTTPS via the merchant backoffice in . Within batch processing not alle functions are available which are usually available for the online interface.
4) PayNow – the Silent Mode
With the PayNow solution the customer enters the data analogue as for the Server-to-Server solution but with the essential difference, that credit card data are transferred directly from the browser (client) to Computop. Above all this saves a lot of effort in the case of complex 3D methods such as Verified by Visa, MasterCard SecureCode and American Express SafeKey. For more details about the PayNow solution see the card processing manual. In order to use this interface the merchant must fulfil the PCI requirement according to SAQ A-EP (https://www.pcisecuritystandards.org/documents/PCI-DSS-v3_2-SAQ-A_EP-rev1_1.pdf).
Principles of programming
The Merchant Interface is designed to accept transactions across the Internet. This interface can be used not only by shops but also by enterprise resource planning systems, for example to initiate payment capture via the after shipment of goods.
To ensure compatibility with programming languages and operating systems, eliminates the need for complex software on the shop server because software installation generally causes problems with operating system versions or safety regulations. Instead, you need only send data via HTML to the - it works in any programming language on any operating system.
Communication with takes place via TCP/IP and HTTP (HyperText Transmit Protocol) with 128 / 256 bit TLS-encryption (HTTPS). Depending on the payment method, a particular Internet page is requested in order to carry out a transaction.
Please note, that the accept only TLS 1.2 or higher as incoming and outgoing traffic.
Accepted cipher:
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
In this homogenous interface, irrespective of the payment method, the same parameters are transmitted in general to these Internet pages so that all payment methods operate in the same way and require no additional effort.
The most important parameters to be submitted to the Internet pages are:
- MerchantID
- Amount and Currency
- URLs for status-messages
The MerchantID is an alphanumerical value which uniquely identifies the merchant within the and is allocated by . The Amount and Currency parameters determine the amount of the payment. You also give an Internet page for your shop which receives the result of the payment: After making the payment, confirms successful payments by calling up URLSuccess and failed payments by calling up URLFailure.
The following list shows a typical example with the parameters for processing a payment:
MerchantID=YourMerchantID&TransID=ab123456&Amount=9000&Currency=EUR&URLSuccess=https://www.shop.de/ok.cgi&URLFailure=https://www.shop.de/failed.cgi&URLNotify=https://www.shop.de/notify.cgi |
Notice: Depending on the implementation, URLSuccess and URLFailure are called up via a Redirect (HTTP Status 302 Object Moved) which is then dependent on the customer's browser. In order to ensure that the shop has been informed correctly about the status of the payment sends a further confirmation via a direct Server-to-Server connection to the shop (URLNotify).
Operating principle of the Merchant Interface
In order to send payment orders to the Merchant Interface a shop connects via Internet to and sends the required payment data in a defined homogeneous format which is based on name-value-pairs (NVP). The Merchant Interface works with HTML and is compatible with all current firewalls, operating systems (Linux, Unix, Windows) and shop systems. Even self-programmed shops can be simply integrated with the interface.
A payment process looks something like the following:
1 The customer selects the payment method in the shop and clicks on the Pay button. 2 The shop generates a character string with merchant number, amount and shopping cart: "MERCHANT=YourMerchantID&AMOUNT=49&SHOPPING CART=Flowers" 3 Depending on the payment method the character string is transmitted to the corresponding Internet page: paySSL.aspx?"MERCHANT=123&Amount=49&SHOPPING CART=Flowers" |
The simple transmission of a character string has the advantage that you need install no software on the shop server. The interface functions with all current payment methods so that a connection to suffices for several payment methods.
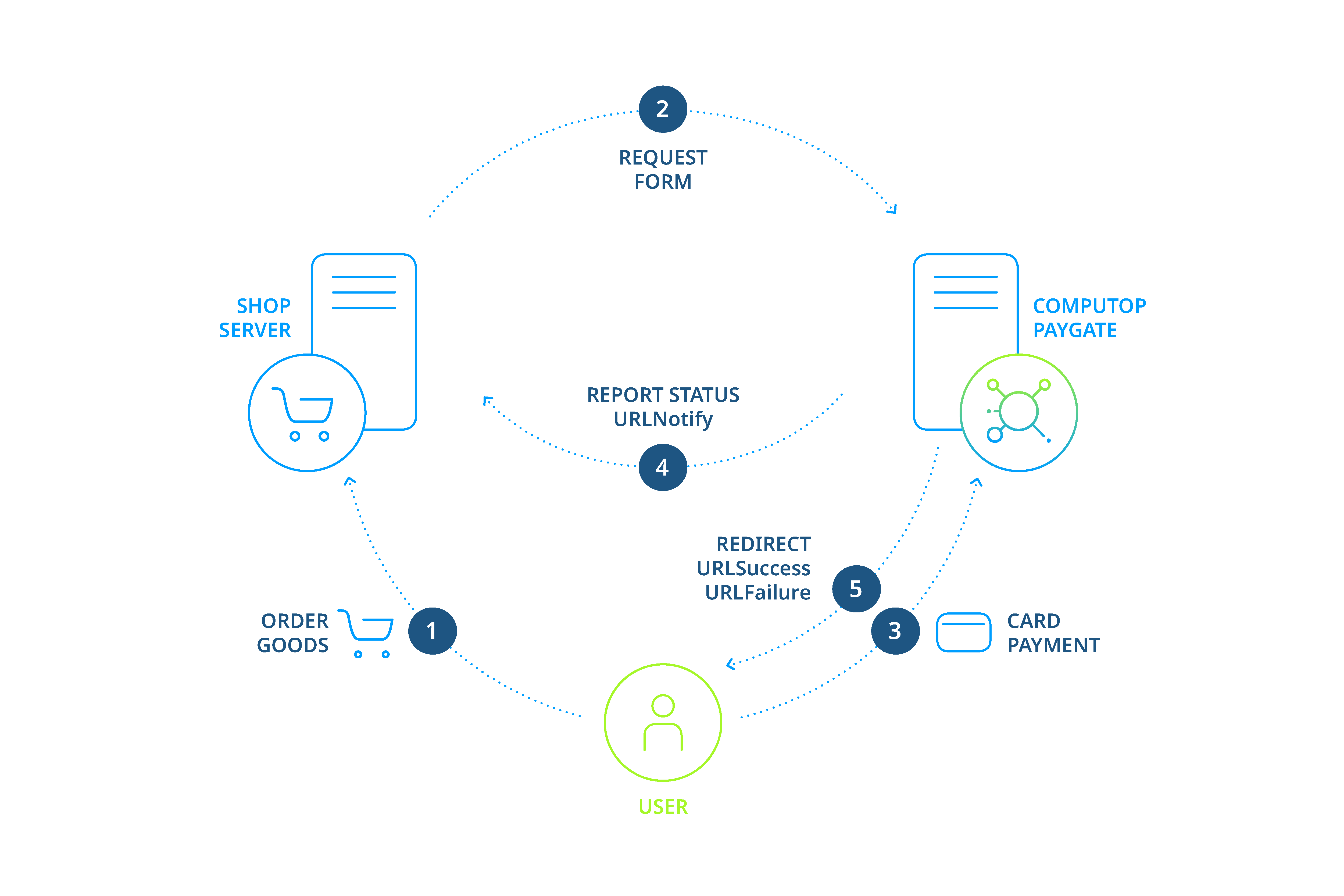
Payments via forms
In the case of payments via forms, the shop redirects its customers to the HTML form where they enter their payment details. then processes the payment and informs the shop about the payment result.
Process of a payment with HTML forms
Process of payment
To make payments via forms you send a request to a Internet page with HTTPS GET or HTTPS POST. The corresponding URL you will find within the manual for the respective payment method.
All details required for payment processing are forwarded as parameters. The parameters are encrypted with Blowfish and protected with HMAC-Authentication (see below) to ensure that neither the customer nor a third party can manipulate the data.
When calling the form decrypts the parameters and shows the HTML page with the entry fields for the corresponding payment type. The customer enters the data and triggers the payment process by clicking the Pay button.
After the payment has been made redirects the customers back to a shop page via HTTPS GET or HTTPS POST (URLSuccess, URLFailure) and transmits the result of the payment as a Blowfish-encrypted parameter string to these URLs. In addition transmits the result via HTTPS POST to the shop's Notify page (URLNotify). The shop accepts the payment result and decrypts the data in order to inform the customer about the status.
Request for a form
The request for a form starts with the correct composition of the parameters which consist of a key and a value which are separated by an equals sign (=). These are so called Name-Value-Pairs (NVP):
MerchantID=YourMerchantID |
All parameters are assembled in a character string and separated by the character &:
Amount=100&Currency=EUR&TransID=12345 |
Notice: Since the characters "=" and "&" are used as separating characters, these characters cannot be transmitted as values. All values which you transmit without BlowFish-encryption must be URL-Encoded.
A correct parameter character string for contains three basic parameters: MerchantID, Len and Data. The parameters MerchantID and Len are unencrypted. Only the Data parameter is Blowfish-encrypted:
MerchantID=YourMerchantID&Len=67&Data=0A67FE96a65d384350F50FF1 |
The Data parameter contains the sensitive payment details such as amount and currency. The encrypted bytes are Hex-encoded and completed to two characters from the left with a zero. Encryption is via Blowfish ECB and is available to you as source-code and components.
The Len parameter is very important for encryption because it contains the length of the unencrypted(!) character string in the Data parameter. Since the data quantity to be encrypted is increased by a multiple of 8 in the case of the Blowfish encryption, the correct length of the character string must be known for decryption. Otherwise accidental characters emerge at the end of the character string.
The parameters are transmitted via HTTPS POST or HTTPS GET. The recommended transmit method is HTTPS POST because the parameter character string in the case of GET is attached to the URL, which is limited to 2048 bytes depending on the browser.
Notice: Please note that the maximum length of a payment request is limited to 5120 characters. If you require longer strings please contact .
The following listings show the development of a payment request. The first listing is the unencrypted parameter character string:
MerchantID=YourMerchantID&TransID=100000001&Amount=11&Currency=EUR&URLSuccess=https://www.shop.de/ok.html&URLFailure=https://www.shop.de/failed.html&URLNotify=https://www.shop.com/notify.cgi&OrderDesc=My purchase |
Notice: Please note that a value is to be assigned to each parameter. Do not transmit empty parameters, as this can cause the payment to fail.
This character string is encrypted and transmitted as the Data parameter. The HTTPS GET request for a form for credit card payments looks like this:
Notice: Please note that the parameters are transmitted unencrypted for the purpose of layout of the form.
An HTML form is produced for HTTPS POST and all parameters are transmitted as Hidden Fields. Only the Pay button is visible to the customer:
Hash MAC-Authentication
To protect against unauthorised manipulation of your payment transactions, the checks with the aid of a Hash Message Authentication Code (HMAC) whether your payment enquiry is authentic and has not been manipulated. For this purpose you transfer an HMAC value to the with each transaction in the parameter MAC.
Background: Unlike the HMAC procedure every encoding method has the disadvantage that there is a matching decoding method. Anyone who possesses the correct key or cracks the encryption can read and manipulate the data. Therefore, no encryption method is ever 100% safe. In the case of the Hash procedure, conversely, decoding is impossible, so that a Hash value can confirm the authenticity of the message free of doubt.
The uses a Hash Message Authentication Code (HMAC) to check the authenticity of your payments. The MAC SHA-256 algorithm is used with a 32-digit key length (256 bits) for this. The additional password makes the HMAC procedure particularly safe.
The following table describes how you can generate the Hash values for your payment:
Step | Task | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Please log on to Computop Support, which supplies you with the Hash password. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2 | The HMAC value is calculated with the aid of the password and several parameter values. For the calculation, the parameters PayID, TransID, MerchantID, Amount and Currency are used and separated with asterisks:
Notice: If a transaction does not support all of these parameters, you can simply omit the missing value. For example, there is no PayID yet with the first transaction, so you do not have to transfer this. The PayID is a component of the Hash calculation in subsequent transactions:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3 | Use the MAC SHA-256 algorithm, which nearly all programming languages support, in order to calculate the Hash value with the password and the parameter values. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4 | Use the MAC parameter to transfer the hexadecimal encoded Hash value to the with each transaction in the encoded data field. |
Notice: Note that the MAC parameter is obligatory for all subsequent transactions (e.g. capture, credit note) if it was transferred with the first transaction (e.g. authorisation).
Important: The rejects transactions with wrong or missing HMAC values promptly without further processing, because this is an indication of hacker attacks. Therefore, transactions which the rejects with the error codes 20100044 or 20120044 do not appear in .
Listing with HMAC examples
|
The shop must verify that a notification request really comes from Computop. Otherwise an attacker can initialise a transaction and then falsify this notification. A shop operator will not manually check whether a corresponding transaction was performed in each case. Therefore, the module must do this automatically.
Currently, the notification request is only encrypted. However, this encryption does not guarantee the authenticity of a message. It only guarantees that a message cannot be listened in on. Therefore, this safety measure is insufficient. As a result, the response parameter MAC is used, which is formed via the same algorithm as the input MAC. Only the data parameters differ. The following data pattern applies here for hash generation: PayID*TransID*MerchantID*Status*Code
The MAC parameter is only returned to the Success or Failure URL and for Notifys.
Important: Passwords may never be send via email, because in this case immediately the security of encrypted Requests/Responses is no longer assured. If accidentally passwords were sent via email, new passwords must be deposited at the merchant's expense with a single process or during next standard release. Computop explicitly point on the risik of further using such compromised MIDs. If a merchant nevertheless continues such a compromised MID, he bears the liability risk for possible losses due to the compromised passwords on his own.
You can check your Blowfish encryption or MAC calculation here : Axepta Platform // Simple Test Tools (paytest.info)
Notification of the shop
After processing the payment notifies the shop of the payment result. To do this calls URLNotify via HTTP POST. This is an entirely separate communication which has nothing to do with the original connection between the shop, the customer and . The parameters are transmitted in the HTTP Body as a Blowfish-encrypted parameter string. The content type is application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=iso-8859-1. Therefore the standard values for HTML-form analysis are used.
Notice: Please note that the Notify-call is permitted only via Port 443 (TLS) for security reasons.
If the shop’s URLNotify is not accessible (e.g. HTTP-status 500/404), notification is repeated 8 times. In this case the customer transmit to the shop is prior to the URLNotify request. Therefore the shop should analyse and compare both status messages from URLNotify and transmission (URLSuccess, URLFailure).
Repeat | Waiting time | Time after 1. Notify |
|---|---|---|
0 | instantly | 0 |
1 | 00:01 h | 00:01 h |
2 | 00:08 h | 00:09 h |
3 | 00:27 h | 00:36 h |
4 | 01:04 h | 01:40 h |
5 | 02:05 h | 03:45 h |
6 | 03:36 h | 07:21 h |
7 | 05:43 h | 13:04 h |
8 | 08:32 h | 21:36 h |
Time of repeat of Notify respectively calculated after first failed attempt
Notice: The URL encoded parameters are transmitted in key-value pairs (Key1=Value1&Key2=Value2). Please note that new parameters can be added unannounced at any time. Therefore, we recommend the use of the parameter name for the analysis, not the order since this can change at any time. Please do not use case sensitive mechanisms for the spelling of the parameters as this can change at any time. For example, it is recommended switching all parameters “to lower” and continuing in lower case.
For more details please go to:
www.w3.org/MarkUp/html-spec/html-spec_8.html#SEC8.2.1
Transfer of the customer to the shop
Once payment is complete, the customer is redirected via HTTP GET back to the shop. then returns an HTTP Status 302 (object moved) and attaches the payment status as Blowfish-encrypted parameters to URLSuccess or URLFailure. Unlike a payment request the payment response contains no MerchantID. The parameters Len and Data have the same function.
Correct testing
Until you have completed the programming your account is in test mode: credit card payments are authorised but there is no cashflow because the has not instigated a capture.
Notice: Please use only small amounts between 0.11 and 2 euros in test mode because the credit card authorisations are genuine even in the test and reduce the limit of your credit card. If you use large amounts and reach the card limit, your credit card will no longer function temporarily.
In the case of successful payments the returns the value zero in the Code parameter. If a payment fails, the Code parameter is greater than zero, for which there may be many reasons: an incorrect expiry date, an exceeded card limit or even a blocked card are just a few examples. You can find a full list of error codes as an Excel-file in the error codes list.
If you wish to test the different error cases, allows you to simulate the desired error codes. To simulate an error, transmit the keyword Test in the OrderDesc parameter followed by the four-digit detailed error code, for example "Test:0110" to simulate an expired credit card. then returns the four-digit detailed error code with the respective response-parameters.
Test case with timeout
A credit card payment is normally completed within one to two seconds. In a few cases however, payments may be terminated due to long processing times in the banking network. terminates credit card payments after 90 seconds. If you prefer shorter timeouts our can configure the termination individually, for example after 45 seconds.
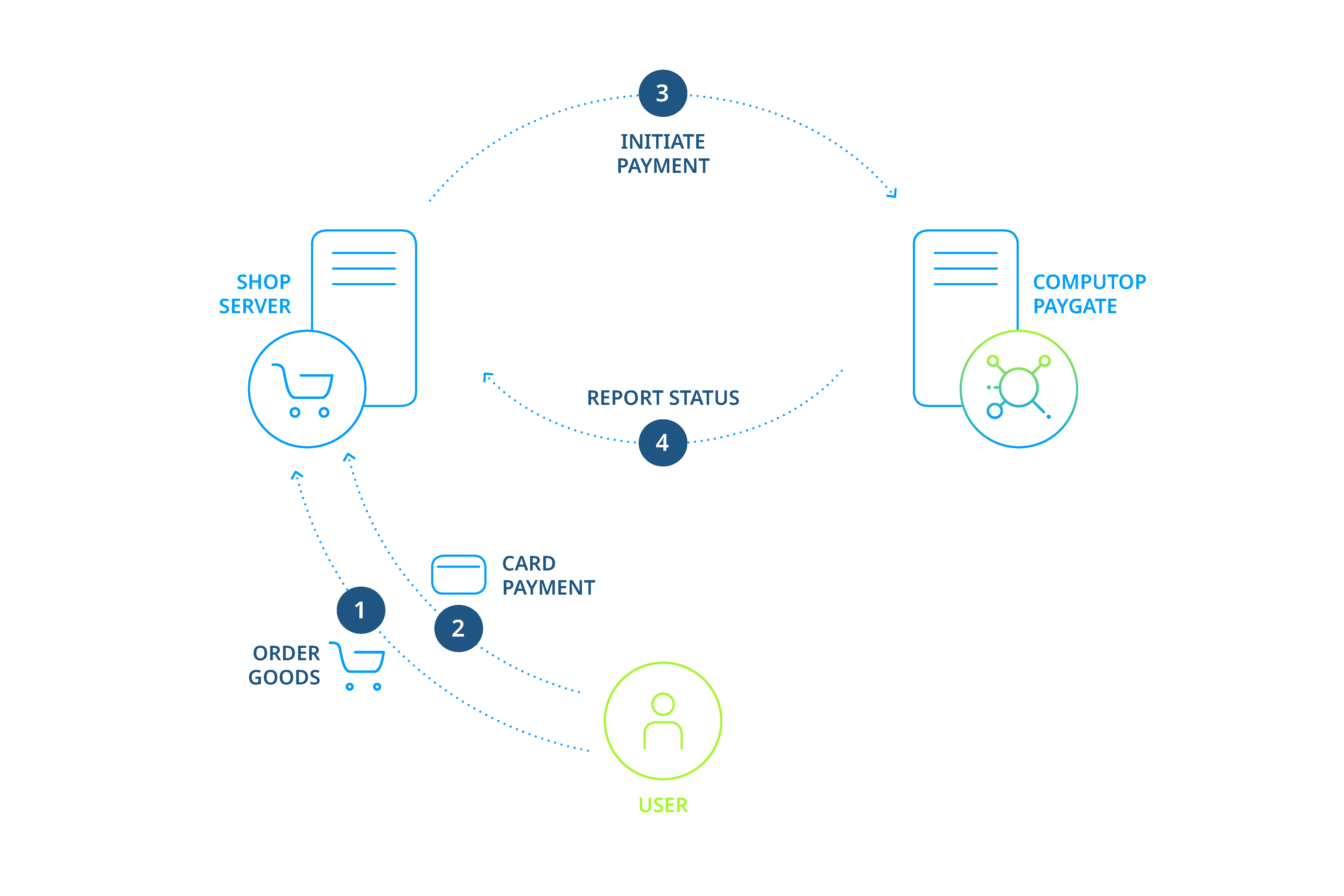
Payments via Server-to-Server connection
In the case of payments via the Server-to-Server connection, the merchant already holds payment details such as credit card numbers and bank account details. Shop or enterprise resource planning systems create a TLS socket-connection to the server in order to carry out a payment transaction.
Process of a Server-to-Server payment
Notice: When processing payments via a Server-to-Server connection your system must control the communication with the automatically. This can be complicated in some cases.
Notice: Please ensure that for one payment (PayID) no multiple requests are submitted simultaneously, because this can lead to errors within transaction processing. Please ensure to have a few seconds between two requests for the same payment/PayID.
Process of a Server-to-Server payment
The request for a payment starts with the correct composition of the parameters which consist of a key and a value and which are separated by an equals sign (=). These are so called Name-Value-Pairs (NVP):
MerchantID=YourMerchantID
All parameters are assembled in a character string and separated by the character &:
Amount=100&Currency=EUR&TransID=12345
Notice: Since the characters "=" and "&" are used as separating characters, these characters cannot be transmitted as values. All values which you transmit without BlowFish-encryption must be URL-Encoded. There is only one exemption from this rule: For credit cards which are registered for Verified/SecureCode/SafeKey/JSecure/ProtectBuy for example the ACSURL is transmitted unencoded.
A correct parameter character string for contains three basic parameters: MerchantID, Len and Data. The parameters MerchantID and Len are unencrypted. Only the Data parameter is Blowfish-encrypted:
MerchantID=YourMerchantID&Len=67&Data=0A67FE96a65d384350F50FF1
The Data parameter contains the sensitive payment details such as amount and currency. The encrypted bytes are Hex-encoded and completed to two characters from the left with a zero. Encryption is via Blowfish ECB and is available to you as source-code and components.
The Len parameter is very important for encryption because it contains the length of the unencrypted(!) character string in the Data parameter. Since the data quantity to be encrypted is increased by a multiple of 8 in the case of the Blowfish encryption, the correct length of the character string must be known for decryption. Otherwise accidental characters emerge at the end of the character string.
The following listings show the development of a payment request. The first listing is the unencrypted parameter character string:
MerchantID=YourMerchantID&TransID=100000001&Amount=11&Currency=EUR&OrderDesc=My purchase&CCNr=1111333355557777&CCCVC=123&CCExpiry=202012&CCBrand=VISA
Notice: Please note that a value is to be assigned to each parameter. Do not transmit empty parameters, as this can cause the payment to fail.
This character string is encrypted with Blowfish:
MerchantID=YourMerchantID&Len=140&Data=D622C5FE7414F73539A1852C2CE7AA0BE904A7E2339DCF9363DA6ACDBE5EF98E169FC3092B1602564DBF2C3C75173A62C484962A247B8A91EA7A544ADCF2A037135421FD0CE092C174A7D1D63517BD45099AC2B682F5E3CD2C942A6F0E741A833C
In order to make payments via a Server-to-Server connection, open a TLS-Socket connection to and transfer the generated character string to the following URL:
direct.aspx |
As soon as the TLS socket connection is made, a normal HTTP POST, version 1.1 is carried out. In this case the following fields are specified in the HTTP header:
Mandatory information within HTTP-header
The HTTP Body contains the parameter character string. Note that the values must be submitted as URL-encoded parameters. The following listing is an example of a credit card payment:
Notice: Please note that the maximum length of a payment request is limited to 5120 characters. If you require longer strings please contact Computop Support.
The following listing shows a typical response. writes the Blowfish-encrypted data into the socket:
HTTP/1.0 200 OK Connection: Close Content-type: text/plain Content-Length: 228 Len=125&Data=ECF59EC63E9BEE74DF217E27FA2E194B92597C7395BADBAD4340CDFD000DD57129EEFAA0BE904A7E233ACDBE5EF98E1692B1602564DBF2C3C75173A62C484962A247B8A91EA7A544
The decrypted response within the Data parameter looks like this:
PayID=a234b678e01f34567090e23d567890ce&XID=50f35e768edf34c4e090e23d567890ce&TransID=100000001&Status=AUTHORIZED&Description=AUTHORIZED&Code=00000000
It is a synchronous communication such that the Socket-connection remains open until has supplied the answer. If a request is not answered within 120 seconds may issue a timeout error message.
Notice: The URL encoded parameters are transmitted in key-value pairs (Key1=Value1&Key2=Value2). Please note that new parameters can be added unannounced at any time. Therefore, we recommend the use of the parameter name for the analysis, not the order since this can change at any time. Please do not use case sensitive mechanisms for the spelling of the parameters as this can change at any time. For more details please go to: